Entity Framework Architecture
The following figure shows the overall architecture of the Entity Framework.
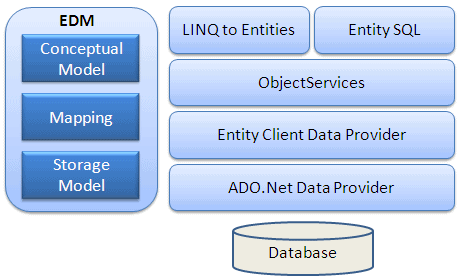
Let's look at the components of the architecture individually.
EDM (Entity Data Model): EDM consists of three main parts - Conceptual model, Mapping and Storage model.
Conceptual Model: The conceptual model contains the model classes and their relationships. This will be independent from your database table design.
Storage Model: The storage model is the database design model which includes tables, views, stored procedures, and their relationships and keys.
Mapping: Mapping consists of information about how the conceptual model is mapped to the storage model.
LINQ to Entities: LINQ-to-Entities (L2E) is a query language used to write queries against the object model. It returns entities, which are defined in the conceptual model. You can use your LINQ skills here.
Entity SQL: Entity SQL is another query language (for EF 6 only) just like LINQ to Entities. However, it is a little more difficult than L2E and the developer will have to learn it separately.
Object Service: Object service is the main entry point for accessing data from the database and returning it. Object service is responsible for materialization, which is the process of converting data returned from an entity client data provider (next layer) to an entity object structure.
Entity Client Data Provider: The main responsibility of this layer is to convert LINQ-to-Entities or Entity SQL queries into a SQL query which is understood by the underlying database. It communicates with the ADO.Net data provider which in turn sends or retrieves data from the database.
ADO.Net Data Provider: This layer communicates with the database using standard ADO.Net.