Configure Many-to-Many Relationships in Code-First
Here, we will learn how to configure a Many-to-Many relationship between the Student and Course entity classes. Student can join multiple courses and multiple students can join one Course.
Visit the Entity Relationship chapter to understand how EF manages one-to-one, one-to-many and many-to-many relationships between entities.
Many-to-Many Relationship by Following Conventions
EF 6 includes default conventions for many-to-many relationships. You need to include a collection navigation property at both ends.
For example, the Student class should have a collection navigation property of Course type, and the Course class should have a collection navigation property of Student type to create a many-to-many relationship between them without any configuration, as shown below:
public class Student { public Student() { this.Courses = new HashSet<Course>(); } public int StudentId { get; set; } [Required] public string StudentName { get; set; } public virtual ICollection<Course> Courses { get; set; } } public class Course { public Course() { this.Students = new HashSet<Student>(); } public int CourseId { get; set; } public string CourseName { get; set; } public virtual ICollection<Student> Students { get; set; } }
The following is the context class that includes the Student and Course entities.
public class SchoolDBContext : DBContext { public SchoolDBContext() : base("SchoolDB-DataAnnotations") { } public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; } public DbSet<Course> Courses { get; set; } protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder) { base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder); } }
EF API will create Students, Courses and also the joining table StudentCourses in the database for the above example.
The StudentCourses table will include the PK (Primary Key) of both tables - Student_StudentId & Course_CourseId, as shown below.
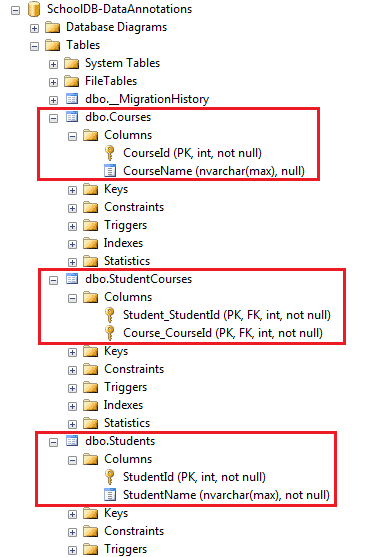
Note: EF automatically creates a joining table with the name of the both entities and the suffix 's'.
Configure a Many-to-Many Relationship using Fluent API
As you have seen above, the default conventions for many-to-many relationships creates a joining table with the default naming conventions. Use Fluent API to customize a joining table name and column names, as shown below:
protected override void OnModelCreating(DbModelBuilder modelBuilder) { modelBuilder.Entity<Student>() .HasMany<Course>(s => s.Courses) .WithMany(c => c.Students) .Map(cs => { cs.MapLeftKey("StudentRefId"); cs.MapRightKey("CourseRefId"); cs.ToTable("StudentCourse"); }); }
In the above example, the HasMany() and WithMany() methods are used to configure a many-to-many relationship between the Student and Course entities.
The Map() method takes Action type delegate, hence, we can pass the lambda expression to customize column names in a joining table.
We can specify the PK property name of Student in MapLeftKey() (we started with the Student entity, so it will be the left table) and the PK of the Course table in MapRightKey() method.
The ToTable() method specifies the name of a joining table (StudentCourse in this case).
The above code will create a joining table StudentCourse with two Primary Keys StudentRefId and CourseRefId which will also be Foreign Keys, as shown below:
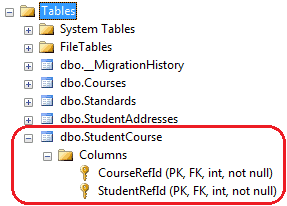
In this way, you can override the default conventions for many-to-many relationship and customize a joining table name and its columns.
