Concurrency in Entity Framework
Here you will learn how to handle concurrency using EF 6 database-first approach for the underlying SQL Server database.
Entity Framework supports optimistic concurrency by default. EF saves entity data to the database, assuming that the same data has not been changed since the entity was loaded. If it finds that the data has changed, then an exception is thrown and you must resolve the conflict before attempting to save it again.
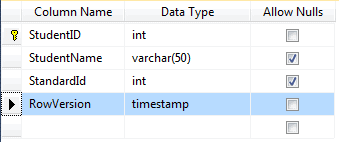
To handle concurrency using EF 6 database-first approach, create a column with rowversion (timestamp) data type in the table in the SQL Server.
The rowversion (synonym timestamp) data type is just an incrementing binary number which is incremented for each insert and update operation performed on a table that contains a rowversion column.
Let's implement concurrency for the Student entity.
In order to check concurrency for the Student entity, the Student table must have a rowversion column.
So, create a new column named RowVersion in the Student table with timestamp data type (timestamp is a synonym data type of rowversion), as shown below:
Now, create a new Entity Data Model as shown in the Create Entity Data Model chapter or, if you already have an EDM, then update it by right clicking on designer -> Update Model From Database -> Refresh Student table.
You will see the RowVersion property added in the Student entity in the designer view.
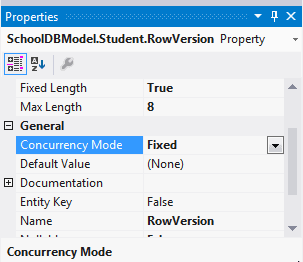
Now, you need to set the concurrency mode to fixed by right clicking on the RowVersion property of the Student entity on the designer, select Property and set Concurrency Mode to Fixed in the property window, as shown below:
EF API will now include this RowVersion column in the where clause in each UPDATE command and if the rowversion value is different than the existing value in the database, then it will throw DbUpdateConcurrencyException.
The following example demonstrates handling concurrency exception:
Student student = null; using (var context = new SchoolDBEntities()) { student = context.Students.First(); } //Edit student name Console.Write("Enter New Student Name:"); student.StudentName = Console.ReadLine(); //Assigns student name from console using (var context = new SchoolDBEntities()) { try { context.Entry(student).State = EntityState.Modified; context.SaveChanges(); Console.WriteLine("Student saved successfully."); } catch (DbUpdateConcurrencyException ex) { Console.WriteLine("Concurrency Exception Occurred."); } }
Assume that there are two users executing the above code. User1 and User2 both get the same Student entity.
Now, User1 enters a new student name and saves it before User2. So, User1 will get a "Student saved successfully" message whereas User2 will get "Concurrency Exception Occurred.".