Spatial Data Type in Entity Framework
MS SQL Server 2008 introduced two spatial data types, geography and geometry.
The geography type represents data in a round-earth coordinate system and geometry represents data in a Euclidean (flat) coordinate system.
Starting with version EF 5.0, it includes special data types in the System.Data.Entity.Spatial namespace:
DbGeography for geography data type and DbGeometry for geometry data type in the SQL Server.
For demo purposes, we have used the Location column from the Course table of geography type in SQL Server database, as shown below:
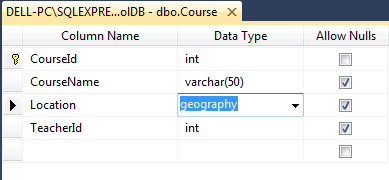
Now, create or update an entity data model (.edmx) after adding the geography column in the database. After creating or updating the EDM, you can see that the Location property of the Course entity is System.Data.Spatial.DbGeography, as shown below:
public partial class Course { public Course() { this.Students = new HashSet<Student>(); } public int CourseId { get; set; } public string CourseName { get; set; } public Nullable<int> TeacherId { get; set; } public System.Data.Spatial.DbGeography Location { get; set; } public virtual Teacher Teacher { get; set; } public virtual ICollection<Student> Students { get; set; } }
You can now use the Location property while adding or updating an entity, as shown below.
using (var ctx = new SchoolDBEntities()) { ctx.Courses.Add(new Course() { CourseName = "New Course", Location = DbGeography.FromText("POINT(-122.360 47.656)") }); ctx.SaveChanges(); }
Visit MSDN for more information on geography data type in MS SQL Server.