Configure One-to-Many Relationships using Fluent API in Entity Framework Core
You learned about the Conventions for One-to-Many Relationship. Generally, you don't need to configure one-to-many relationships because EF Core includes enough conventions which will automatically configure them. However, you can use Fluent API to configure the one-to-many relationship if you decide to have all the EF configurations in Fluent API for easy maintenance.
Entity Framework Core made it easy to configure relationships using Fluent API.
Consider the following Student and Grade classes where the Grade entity includes many Student entities.
public class Student { public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int CurrentGradeId { get; set; } public Grade Grade { get; set; } } public class Grade { public int GradeId { get; set; } public string GradeName { get; set; } public string Section { get; set; } public ICollection<Student> Students { get; set; } }
Configure the one-to-many relationship for the above entities using Fluent API by overriding the OnModelCreating method in the context class, as shown below.
public class SchoolContext : DbContext { protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder) { optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer("Server=.\\SQLEXPRESS;Database=EFCore-SchoolDB;Trusted_Connection=True"); } protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder) { modelBuilder.Entity<Student>() .HasOne<Grade>(s => s.Grade) .WithMany(g => g.Students) .HasForeignKey(s => s.CurrentGradeId); } public DbSet<Grade> Grades { get; set; } public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; } }
In the example above, the following code snippet configures the one-to-many relationship:
modelBuilder.Entity<Student>() .HasOne<Grade>(s => s.Grade) .WithMany(g => g.Students) .HasForeignKey(s => s.CurrentGradeId);
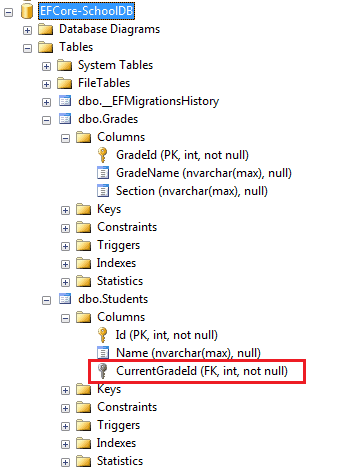
Now, to reflect this in the database, execute migration commands, add-migration <name> and update-database. The database will include two tables with One-to-Many relationship as shown below.
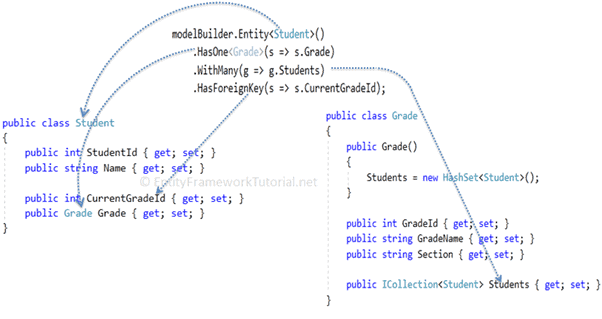
Let's understand the above code step by step.
- First, we need to start configuring with one entity class, either
StudentorGrade. So,modelBuilder.Entity<Student>()starts with theStudententity. - Then,
.HasOne<Grade>(s => s.Grade)specifies that theStudententity includes aGradetype property namedGrade. - Now, we need to configure the other end of the relationship, the
Gradeentity. The.WithMany(g => g.Students)specifies that theGradeentity class includes manyStudententities. Here,WithManyinfers collection navigation property. -
The
.HasForeignKey<int>(s => s.CurrentGradeId);specifies the name of the foreign key propertyCurrentGradeId. This is optional. Use it only when you have the foreign keyIdproperty in the dependent class.
The following figure illustrates the above steps:
Alternatively, you can start configuring the relationship with the Grade entity instead of the Student entity, as shown below.
modelBuilder.Entity<Grade>() .HasMany<Student>(g => g.Students) .WithOne(s => s.Grade) .HasForeignKey(s => s.CurrentGradeId);
Configure Cascade Delete using Fluent API
Cascade delete automatically deletes the child row when the related parent row is deleted.
For example, if a Grade is deleted, then all the Students in that grade should also be deleted from the database automatically.
Use the OnDelete method to configure the cascade delete between Student and Grade entities, as shown below.
modelBuilder.Entity<Grade>() .HasMany<Student>(g => g.Students) .WithOne(s => s.Grade) .HasForeignKey(s => s.CurrentGradeId) .OnDelete(DeleteBehavior.Cascade);
The OnDelete() method cascade delete behavior uses the DeleteBehavior parameter. You can specify any of the following DeleteBehavior values, based on your requirement.
- Cascade : Dependent entities will be deleted when the principal entity is deleted.
- ClientSetNull: The values of foreign key properties in the dependent entities will be set to null.
- Restrict: Prevents Cascade delete.
- SetNull: The values of foreign key properties in the dependent entities will be set to null.